Voltage Regulator
In areas with unstable power supplies, a voltage regulator for 220V AC is essential to protect electrical devices from damage. This device keeps the output voltage steady even when the input voltage changes. Using mechanisms like transformers or electronic circuits, the regulator adjusts itself to maintain the desired output voltage (usually 220V AC), ensuring that equipment receives a stable power supply.
Voltage regulators are essential in various electrical systems, from homes to businesses to factories. They’re used to provide steady power to important devices like computers, medical equipment, and industrial machines, even when the main power source fluctuates. By keeping the voltage stable, regulators prevent damage and ensure continuous operation in areas where voltage changes are frequent.

Component Required:
- BT-136 TRIAC
- DB3 DIAC
- 680k Ohm Resistor
- 100 Ohm Resistor
- 470 Ohm Resistor
- 500K Potentiometer
- 104J2E Capacitor
- Power supply 220v AC
Circuit Diagram:
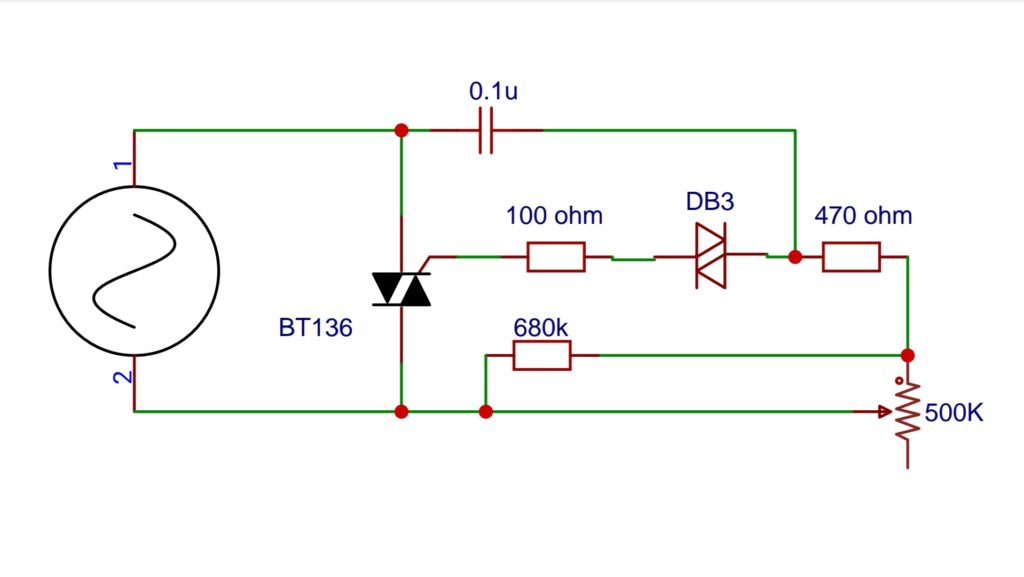
BT-136 (TRIAC):
The BT136 is a triac, a type of semiconductor that controls alternating current (AC) power. Triacs are unique because they can conduct electricity in both directions. In the BT136, “BT” means “Bidirectional Triode,” reflecting its ability to switch on and off in either direction like a triode vacuum tube. The BT136 has three terminals: MT1 (Main Terminal 1), MT2 (Main Terminal 2), and G (Gate). When a small signal is applied to the gate terminal, the triac switches on, allowing electricity to flow between MT1 and MT2 in both directions. This makes it useful for controlling moderate power levels in AC circuits.
The BT136 is a versatile electronic component often employed in scenarios where precise control of alternating current (AC) power is needed. This includes applications such as light intensity adjustment in dimmers, regulating the speed of motors, controlling temperature in heating systems, and switching AC power on or off. The BT136 operates by precisely controlling when electricity flows by using a specific signal. This allows it to regulate the amount of power delivered to devices or systems, effectively enabling control over output voltage or power. As a result, the BT136 triac is a compact, efficient, and dependable device for managing AC power in various electronic and electrical applications.


DB3 DIAC:
The DB3 DIAC is an electronic component used in circuits to activate thyristors and triacs. “DIAC” stands for “diode for alternating current,” and the DB3 is a common type. It acts as a bidirectional switch, triggered by voltage. Unlike regular diodes, the DB3 has no polarity, allowing current to flow in both directions once a specific voltage (threshold) is met. Physically, it looks like a diode with two leads connected to a semiconductor device.
The DB3 DIAC works because of its “negative resistance.” When the voltage on the DIAC reaches a certain level (usually around 30 volts), it quickly switches from being very resistant to being very easy to pass through. This makes it useful for starting up other semiconductor devices, like thyristors and triacs. The DB3 DIAC is used in things like phase control circuits, lamp dimmers, motor speed controllers, and electronic switches. When used with a trigger circuit, the DB3 DIAC allows for precise control over the timing and length of electrical pulses, making it useful in many electronic systems that need to switch and control accurately.
Potentiometers:
Potentiometers are resistors that you can adjust by hand to change the electrical resistance in a circuit. They have a long, narrow piece of material that can conduct electricity (the resistive element). A movable part called a wiper slides along this element. As you move the wiper, the resistance between the wiper and the other ends of the potentiometer changes. This allows you to fine-tune voltage, current, or signal levels in a circuit. For example, potentiometers are used in volume controls for audio devices. When you turn the knob, you’re changing the position of the wiper, which changes the resistance in the circuit that goes to the amplifier. This controls how loud the sound is.
Potentiometers are commonly utilized in measuring and controlling devices for adjusting and calibrating settings. They are used in equipment like temperature regulators, light dimmers, motor speed controllers, and voltage stabilizers. There are various types of potentiometers, such as rotary (rotational dials), slide (linear controllers), and trimmer (small, adjustable components). Each type caters to different applications based on factors like space limitations, accuracy needs, and environmental conditions.
Potentiometers are essential parts in electronic devices because they allow for easy adjustment of different parameters. By using potentiometers, you can fine-tune the behavior of a circuit to meet your specific needs. Their flexibility and control capabilities make them crucial for a wide range of electronic systems and applications.


Resistor:
A resistor is a basic electronic part that blocks the flow of electricity. It’s widely used in electronics and electricity to control the amount of electricity flowing through a circuit, lower voltage, split voltage, end signal paths, change signal levels, and much more. Resistors have a resistance value measured in ohms (Ω) that shows how much they block the flow of electricity. This value affects the voltage drop across the resistor for a given current flow, as described by Ohm’s Law (V = I * R), where V is voltage, I is current, and R is resistance.
Resistors are electronic components that come in different forms to meet the needs of various applications. Fixed resistors have a set resistance value, while variable resistors like potentiometers and rheostats allow for manual or electrical adjustment of resistance. There are different types of fixed resistors, including carbon composition, metal film, and wire-wound resistors. Each type has specific properties and is suitable for different uses depending on factors like accuracy, power handling capacity, sensitivity to temperature changes, and stability. In summary, resistors play a crucial role in electronic circuits. They regulate and stabilize voltage and current flow, enabling electronic devices and systems to function properly.
More Projects:
-
Audio Level Indicator – VU Meter
The VU meter—short for “volume unit meter”—is a device used to measure the average level of audio signals in terms of their loudness. It visually indicates the intensity of sound …
-
Powerful Audio Amplifier Using cd4440
Welcome to our latest video where we delve into the fascinating world of audio amplification using the CD4440 IC! In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through the step-by-step process …
-
Building an Automatic Dark Sensor with BD139 Transistor
Light and darkness are two sides of the same coin, influencing our daily lives in ways we often overlook. Imagine a world where lights adjust themselves according to the ambient …