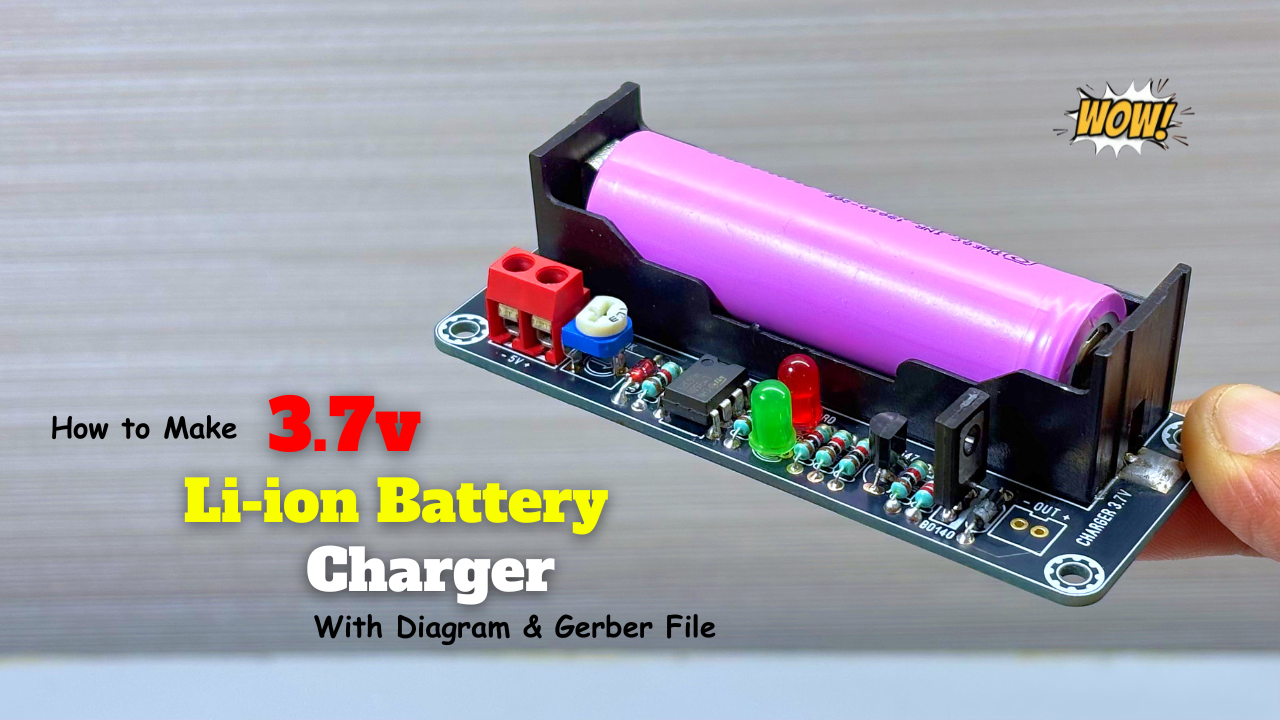
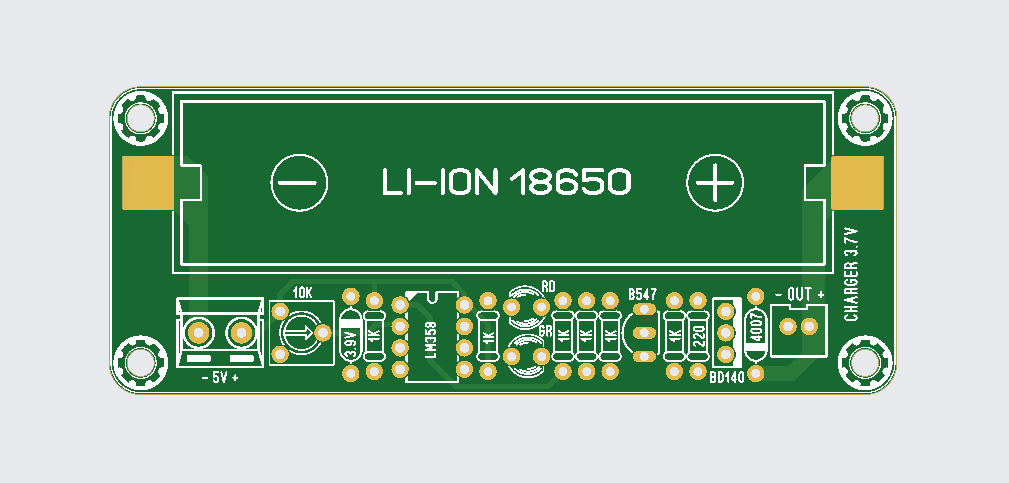
A 3.7 V lithium-ion charger using LM358 is a classic DIY solution and great for learning battery charging fundamentals. Below is a clear, practical explanation + working concept.
Charging a 3.7 V Li-ion / Li-Po battery safely is very important. Over-charging above 4.2 V can damage the battery or even cause fire. In this project, we use the LM358 dual op-amp IC as a voltage comparator to automatically stop charging when the battery reaches 4.2 V.
To build an automatic dark sensor using the BD139 transistor, you’ll need
- IC 741
- BD140 Transistor
- BC547 Transistor
- 1N4007 Diode
- 3.9v Zener diode
- 10K potentiometer
- 1k ohm resistor * 6
- 220 ohm resistors
- Red led
- Green led
- Battery
- Battery holder
- Power Supply 5v
Gerber File:
Special Thanks to Our Sponsor – JLCPCB:
No project is complete without the right tool and materials. That’s why our sponser JLCPCB stepped into provide essential material for the project. JLCPCB is a leading provider of high quality printed circuit board and PCB assembling services.
Simply head over to JLCPCB, Upload your gerber file, select specification and just place your order.
48-Hour Turnaround for 6 Layer PCBs!
$0 for 2u” ENIG. Free Via-in-Pad. High Precision. Sign Up to Get $80 New User Coupons.
How To Order PCB
LM358 IC: The Most Popular Dual Op-Amp for DIY Electronics
If you’ve ever built a sensor circuit, audio amplifier, or Arduino project, chances are you’ve already used the LM358—even if you didn’t realize it. The LM358 is one of the most widely used operational amplifier (op-amp) ICs, especially in low-power and single-supply applications.
Let’s break down what LM358 is, why it’s so popular, and how you can use it in real projects.
What is LM358?
The LM358 is a dual operational amplifier IC, meaning it contains two independent op-amps inside a single 8-pin package. It is designed to operate from a single power supply, which makes it ideal for battery-powered and microcontroller-based projects.
📦 Package: DIP-8 / SOIC-8
⚡ Supply: Single or dual supply
🔧 Cost: Very low (budget-friendly)
Why LM358 Is So Popular
The LM358 stands out because of these key features:
- ✔️ Works with single supply (3V–32V)
- ✔️ Input range includes ground (0V)
- ✔️ Low power consumption
- ✔️ Cheap and easily available
- ✔️ Stable and beginner-friendly
That’s why you’ll find it in Arduino modules, sensor boards, power supplies, and audio circuits.
LM358 Pin Configuration
Here’s the standard 8-pin LM358 pinout:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Output 1 | Output of Op-Amp 1 |
| 2 | Inverting Input 1 | (–) input of Op-Amp 1 |
| 3 | Non-Inverting Input 1 | (+) input of Op-Amp 1 |
| 4 | VCC– | Ground (0V) |
| 5 | Non-Inverting Input 2 | (+) input of Op-Amp 2 |
| 6 | Inverting Input 2 | (–) input of Op-Amp 2 |
| 7 | Output 2 | Output of Op-Amp 2 |
| 8 | VCC+ | Positive supply |
Electrical Specifications (Typical)
- Supply Voltage:
- Single: 3V to 32V
- Dual: ±1.5V to ±16V
- Input Offset Voltage: ~2 mV
- Bandwidth: ~1 MHz
- Slew Rate: 0.3 V/µs
- Operating Temperature: –40°C to +85°C
⚠️ Note: LM358 is not rail-to-rail output, so the output won’t reach full VCC.
Common LM358 Configurations
1. Voltage Amplifier
Used to amplify weak signals from sensors like:
- LDR
- Microphone
- Gas sensor
- IR sensor
2. Comparator
LM358 can work as a comparator for:
- Battery level indicator
- Over-voltage protection
- Threshold detection
3. Buffer (Voltage Follower)
Perfect for:
- Impedance matching
- Protecting microcontroller ADC pins
Simple LM358 Amplifier Example
Non-Inverting Amplifier Gain Formula:Gain=1+R1R2
Example:
- R1 = 10kΩ
- R2 = 100kΩ
- Gain ≈ 11×
LM358 vs LM741 (Quick Comparison)
| Feature | LM358 | LM741 |
|---|---|---|
| Single supply | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Low power | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Modern usage | ✅ High | ❌ Outdated |
| Arduino friendly | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
👉 LM358 easily beats LM741 for modern electronics projects.
Real-World Applications
- Arduino sensor modules
- Audio pre-amplifiers
- Battery voltage monitors
- Signal conditioning circuits
- Power supply feedback loops
- DIY electronics projects
Limitations of LM358
No IC is perfect. Keep these in mind:
- ❌ Low slew rate (not ideal for high-speed signals)
- ❌ Not rail-to-rail output
- ❌ Not suitable for high-quality audio
For better performance, consider LMV358, TL072, or OPA2134.
BC547 Transistor
The BC547 is a general-purpose NPN transistor made from silicon. It is mainly used where small signals need to be amplified or controlled. Because of its low cost, reliability, and availability, it is one of the most popular transistors in the world.
Basic Information
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Type | NPN BJT |
| Package | TO-92 |
| Material | Silicon |
| Operation | Amplifier / Switch |
| Polarity | NPN |
Pin Configuration (TO-92)
When the flat side faces you and the legs point downward:
Base (B) – Control terminal
- Emitter (E) – Current exits
⚠️ Pin order may vary slightly by manufacturer, so always check the datasheet.
⚙️ Working Principle
The BC547 works on the principle of current amplification.
🔹 Basic Rule
A small current at the Base controls a large current between Collector and Emitter.
🟢 Switch Mode
- Base current = OFF → No C-E current
- Base current = ON → C-E current flows
Used for:
- LED ON/OFF control
- Relay driving (small relays)
- Digital switching
🔵 Amplifier Mode
- Weak AC signal applied at base
- Strong amplified signal obtained at collector
Used in:
- Audio amplifiers
- Microphone circuits
- Sensor signal amplification
📊 Electrical Characteristics
| Parameter | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Vceo (Max Collector-Emitter Voltage) | 45 V |
| Ic max (Collector Current) | 100 mA |
| hFE (Current Gain) | 110 – 800 |
| Power Dissipation | 500 mW |
| Transition Frequency (ft) | ~300 MHz |
🔈 Gain Classification
BC547 comes in three gain versions:
| Type | Gain (hFE) |
|---|---|
| BC547A | 110 – 220 |
| BC547B | 200 – 450 |
| BC547C | 420 – 800 |
✔ Higher gain = better amplification
🧪 Applications of BC547
✔ Audio pre-amplifiers
✔ Signal amplifiers
✔ Microcontroller interfacing
✔ Relay driver circuits
✔ Light & temperature sensors
✔ FM transmitter circuits
✔ Logic switching circuits
🔄 BC547 vs Similar Transistors
| Transistor | Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| BC547 | NPN | Low noise, general purpose |
| BC548 | NPN | Lower noise than BC547 |
| BC549 | NPN | Ultra-low noise |
| 2N3904 | NPN | American equivalent |
| C1815 | NPN | Audio application |
More Projects
-
Building an Automatic Dark Sensor with BD139 Transistor
Light and darkness are two sides of the same coin, influencing our daily lives in ways we often overlook. Imagine a world where lights adjust themselves according to the ambient …
-
Safely Assembling 24V 100Ah Battery Pack – Step by Step!
Building an 8S (8 series) LiFePO4 battery pack using LiFePO4 cells and a Daly Battery Management System (BMS). If you’re planning your own DIY power storage project, this guide might …
-
How to Make 3.7v Li-ion Battery Charger
A 3.7 V lithium-ion charger using LM358 is a classic DIY solution and great for learning battery charging fundamentals. Below is a clear, practical explanation + working concept. Charging a …