Light and darkness are two sides of the same coin, influencing our daily lives in ways we often overlook. Imagine a world where lights adjust themselves according to the ambient light—a realm where darkness triggers illumination automatically. Such a world isn’t far-fetched, and with the BD139 transistor, creating an automatic dark sensor becomes an exciting possibility.
The BD139, a versatile and widely used NPN transistor, is an essential component in crafting light-sensitive circuits. When paired with other electronic elements, it can form the foundation of a simple yet efficient automatic dark sensor.
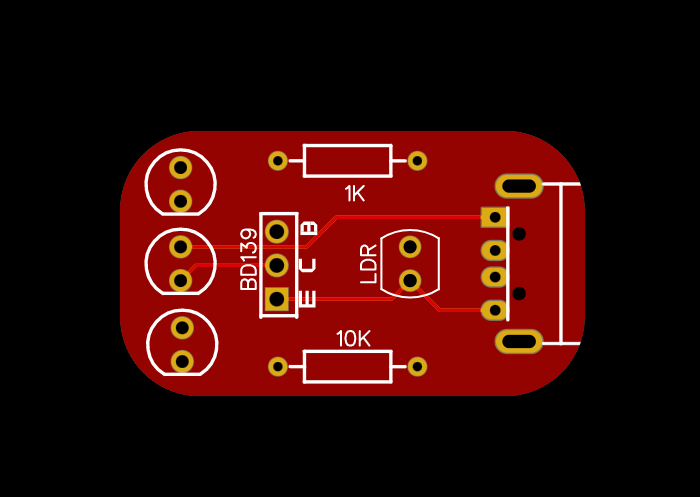
To build an automatic dark sensor using the BD139 transistor, you’ll need
– BD139 transistor
– LDR (Light Dependent Resistor)
– Resistor 10K Ohm & 1k Ohm
– Power supply (battery or DC power source)
– LED or relay
How it Works:
– The LDR’s resistance varies with light intensity. In bright light, the resistance drops, allowing current to pass through the base of the BD139.
– As a result, the transistor conducts, enabling the collector-emitter path and powering off the connected LED or relay in well-lit conditions.
– In darkness, the LDR’s resistance increases, reducing the current flow through the base of the transistor. Consequently, the transistor switches off, activating the LED or relay due to the absence of the collector-emitter path.
Gerber File:

Special Thanks to Our Sponser – JLCPCB:
No project is complete without the right tool and materials. That’s why our sponser JLCPCB stepped into provide essential material for the project. JLCPCB is a leading provider of high quality printed circuit board and PCB assembling services.
Simply head over to JLCPCB, Upload your gerber file, select specification and just place your order.
JLCPCB PCB Fab & Assembly from $2! Sign up to Get $60 Coupons
Sign Up to Get $60 New User Coupons.
How To Order PCB
Circuit Diagram:
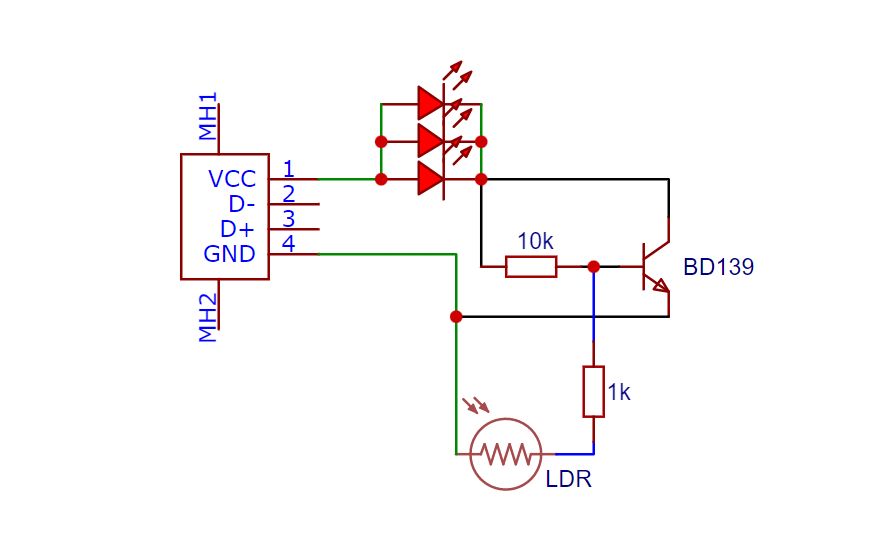
Conclusion:
The automatic dark sensor built around the BD139 transistor and the LDR showcases the magic of electronics in responding to environmental changes. This simple circuit, using components readily available to hobbyists and electronics enthusiasts, illustrates how technology can adapt to natural light fluctuations, offering convenience and efficiency in various applications.
Experimenting with this circuit can lead to modifications and enhancements, allowing for tailored solutions in areas like security systems, energy conservation, and more. The BD139 transistor, with its reliability and adaptability, continues to be an invaluable asset in crafting innovative electronic designs that seamlessly integrate with our surroundings.
BD139
The BD139 is a type of bipolar junction transistor (BJT) that falls under the category of NPN (negative-positive-negative) transistors. It is widely used in various electronic circuits due to its versatility, reliability, and ease of implementation.
Key specifications of the BD139 include:
- Polarity: It’s an NPN transistor, meaning it conducts when a small current flows into its base.
- Pin Configuration: The BD139 transistor typically has three pins—Emitter (E), Base (B), and Collector (C).
- Current and Voltage Ratings: It’s capable of handling moderate to high currents and voltages, making it suitable for various applications.
Applications:
- Commonly used in amplification circuits, switching circuits, and as a general-purpose transistor in electronic projects.
- The BD139, being an NPN transistor, operates by allowing a small current to flow from the base to the emitter, controlling a larger current flowing from the collector to the emitter. This property makes it useful in amplification and switching tasks within electronic circuits.
- It’s often utilized in a wide range of projects by hobbyists, engineers, and electronic enthusiasts due to its availability, affordability, and capability to handle various tasks within electronic systems.
LDR
An LDR, or Light Dependent Resistor, is a type of resistor whose resistance changes with the amount of light falling on it. Also known as a photoresistor or photocell, an LDR’s resistance decreases as the intensity of light increases and vice versa.
Construction:
An LDR typically consists of a semiconductor material whose conductivity varies based on the light it receives. This semiconductor’s properties cause the resistance to change when exposed to light or darkness.
How it Works:
When light falls on the LDR, photons excite electrons in the semiconductor material, causing more electrons to flow freely, thereby reducing the resistance. In darkness or low light conditions, fewer photons interact with the semiconductor material, resulting in higher resistance.
Applications:
- Light Sensing: LDRs are commonly used in light sensing circuits, such as automatic streetlights, where the change in resistance triggers a response, like turning the lights on or off based on ambient light levels.
- Security Systems: They are also used in security systems to detect changes in ambient light, triggering alarms or activating cameras when there’s a sudden decrease in light (indicative of an intruder switching off lights).
- Camera Exposure Control: LDRs have been used in older camera systems to measure ambient light and adjust the camera’s aperture or shutter speed accordingly for proper exposure.
Characteristics:
- Sensitivity: LDRs can be sensitive to various wavelengths of light depending on their composition, making them useful in different light detection scenarios.
- Response Time: They typically have a slower response time compared to other light sensors like photodiodes, which may limit their use in certain fast-response applications.
- LDRs are affordable, easy to use, and adaptable to various light-dependent applications, making them popular components in many electronic projects and sensor-based systems.
-
Building an Automatic Dark Sensor with BD139 Transistor

Light and darkness are two sides of the same coin, influencing our daily lives in ways we often overlook. Imagine a world where lights adjust themselves according to the ambient …
-
Safely Assembling 24V 100Ah Battery Pack – Step by Step!

Building an 8S (8 series) LiFePO4 battery pack using LiFePO4 cells and a Daly Battery Management System (BMS). If you’re planning your own DIY power storage project, this guide might …
-
How to Make 3.7v Li-ion Battery Charger
A 3.7 V lithium-ion charger using LM358 is a classic DIY solution and great for learning battery charging fundamentals. Below is a clear, practical explanation + working concept. Charging a …